Aging
Article curated by Ed Trollope
Ageing is an inevitable part of life. And yet scientists don't really understand how, or why, we age. It's thought that a combination of pre-programmed bodily changes and environmental issues are responsible, but how these interact isn't clear[1]. Some researchers are trying to help us make better lifestyle choices to extend our healthy life span[2], while others look for a way to stop the ageing process in its tracks[3].

Why do we age?






 2
2
Other theories about free radicals and ageing say the opposite: the theory of hormesis holds that low levels of free radicals/reactive oxygen species are essential for longevity because they cause low level oxidative stress and thus initiate an adaptive response in cells, making them better able to cope with future stress. The theory is that this is why exercise and dietary restrictions can improve longevity. So until further studies provide conclusive evidence, the link between free radicals and ageing remains elusive. In particular, although studies have linked free radicals inside mitochondria to ageing, using a circularly permuted yellow fluorescent protein, cpYFP, as a free radical detector, other work has shown that this detector doesn't actually measure the free radicals it's supposed to. Instead the signals of the probe are the result of changes in pH (acidity) inside mitochondria. How pH is related to ageing is yet to be explored.

 2
2Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of cells. Mitochondrial function clearly deteriorates with increasing age and many studies in yeast and metazoans have suggested this causes aging too. The underlying mechanisms are unknown[7]. A new study indicates that, in yeast, an age-dependent loss of acidity in the cell vacuole leads to mitochondrial dysfunction; but the mechanism surprised researchers: instead of upsetting the process of breaking down waste, they found the mitochondria no longer stored amino acids, the building blocks of DNA, well[8].

TelomeresThroughout our lives, as we grow, change and heal, our DNA replicates itself, and cells divide. This is a difficult process, and each time it occurs, the very ends of each chromosome is missed. This would be really bad news if it meant that information was lost during each cell division, but luckily, nature has a solution. The end section of each chromosome is a telomere – a section of repeating nucleotides which protect the rest of the chromosome. In some cells like stem cells, an enzyme replenishes the telomeres after division! But not all. This limits the number of times the cell can divide. We don't know whether shortening telomeres causes the symptoms of ageing, but researchers are looking into resisting it[9].


 2
2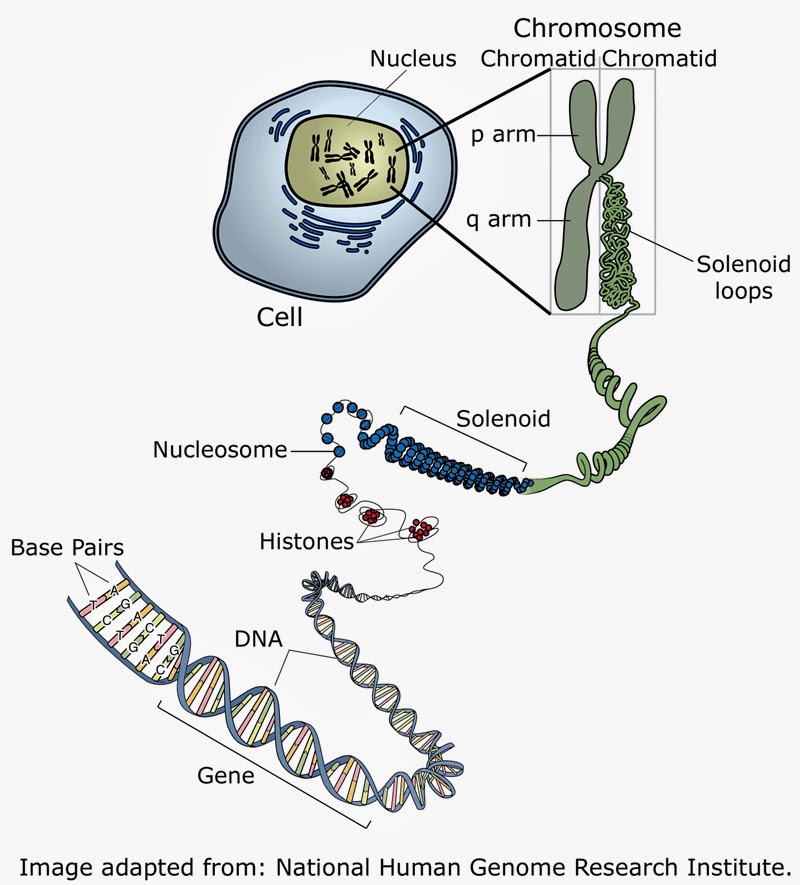
Telomerase is an enzyme that prevents the telomere from shortening during cell division. Its presence therefore prolongs the life of the cell. In some cases this is good as it allows cells we need to regenerate. But, in cancer cells, it allows them to regenerate and the cancer to spread. So some researchers are looking at introducing telomerase to cells, and other into suppressing it!

Stem cell theory Stem cells have the job of regrowing cells when they become damaged or worn, and exist in different amounts round the body. The stem cell theory of aging suggests that aging might arise from stem cell degradation or loss of function. When this happens, damaged or faulty cells in the body are not always replaced, and thus aging arises from lack of regeneration rather than accumulation of damage per se. The theory is supported by the finding that younger people have many more stem cells than older people, but that cell damage rate is independent of age. However, it could be the secondary consequence of another aging mechanism too – we don't yet know.


Longevity
While some scientists are trying to discover why we age, others are want to know why some people live to 100, without living particularly healthy lifestyles! Perhaps the difference is down to their DNA[10]. Afterall, we know people react differently to different drugs and lifestyles, but isolating the genes responsible is a mammoth task. In many cases, a combination of genetics and environmental influences leads to a disease[11]. One day, genetic testing may lead to personalised medicine, and we can already test for risky genes, like those associated with breast cancer[12][13].


 2
2Smoking increases your chances of throat and lung cancers, heart disease, and even accelerates ageing. But some smokers are long-lived. People often believe this is a fluke of chance, and they themselves may be one such lucky smoker. However, research suggests it could in fact be genetic. In particular, single nucleotide polymorphisms, single changes in the base positions within DNA, were found in long-lived smokers, but not of more short-lived smokers. These kinds of changes occur in everyone's DNA, but where they turn up matters. These individuals had a 22% increased chance of making 90, 11% lower risk of cancer, and were three times as likely to make their hundredth birthday!






 3
3
Brain age
![Lateral View of the Brain By BruceBlaus [CC BY 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](/img/sci/Blausen_0101_Brain_LateralView_512.png)


Interestingly, some people's brains seem not to be affected by age in the way most others are. These so-called super-agers show similar patterns of brain activity to younger participants in memory tasks, and they don’t show the same shrinkage in memory-related brain areas seen in most older people. Unfortunately, we don’t yet know why some people seem safe from cognitive decline, but it is likely to be at least partly down to their genes.


 2
2We are often told that in your mid-20s, your brain reaches it’s peak… but it’s not quite this simple. While speed of processing and working memory do seem to decline fairly early, some skills, such as vocabulary and general knowledge, often improve over time and do not decline until people are quite elderly. The ability of the brain to change (plasticity) is thought to decrease with age, although this doesn’t mean you can’t learn new things after a certain age, only that it is more difficult. And again, it varies depending on the skill – basic sensory or motor abilities have more limited plasticity windows than higher-level cognitive skills – and with individuals, who experience declines at different rates. We know that highly educated people, and those that keep learning as they get older, tend to experience less dramatic declines. One theory is that their densely packed neural synapses, formed through learning, protect against cognitive impairment.


 2
2However, research conflicts over whether performing mental exercises can delay the onset of Alzheimer's and similar memory loss related degradation, but physical exercise definitely helps. Why is this? Some think it may be that our understanding of what is mental exercise varies and only some kinds of tasks help whilst others don't, or that you need to keep your brain active your whole life, not just start exercising it in your old age. So is it normal to experience lapses in memory as we get older? Unfortunately, yes. Episodic memory seems to decline more with age than semantic or procedural – this is why you might forget where you left your keys, or what you went upstairs for. However different testing and control methods have given different results – some seeing declines starting in the 20s, others not until the 60s! Brain scanning studies have found a range of differences between older and younger adults; for example, the brain can actually lose brain cells with age, the cortex becomes thinner, and important regions like the hippocampus shrink[15]. A decrease in blood flow to the brain may be partially to blame for the decline.


 2
2
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia and affects almost half a million people in the UK alone – and the number is rising[16] ...Despite being identified in the early 20th century, we are still not exactly certain why some of us will develop Alzheimer’s while others will not.
Learn more about Causes of Alzheimer's Disease.


 2
2Scientists generally agree that long-term memories are encoded in synapses, according to differences in their signalling strength. However, research has shown that this may not be the case, and that in fact memories may be stored in the nuclei of neurons and be modifiable by epigenetics. This has been demonstrated in marine snails, when researchers taught snails to enhance their defence reflex from 1 to 50 seconds using mild electric shocks, then extracted their RNA and injected it into untrained snails. The injected snails were tested, and withdrew for 40 seconds. If translatable to humns, findings could not only lead to potential memory repair/restoration/replacement therapies for patients with diseases such as Alzheimer’s and post traumatic stress, they could even reframe the way we understand “instincts” – as perhaps resident RNA fragments from our ancestors.


 2
2Research from Beijing, Yale and Peking universities has linked air pollution and human cognitive decline. The work, which involved performing verbal and mathematical skills testing on 25,000 Chinese people of all ages and genders, linked nitrogen, sulfur dioxide and fine particulate matter concentrations in their area to decline in test scores, with the results most pronounced in less educated males. Researchers believe that the results are causational since the effect becomes more pronounced with age, although they do not know which pollutant may be the cause: indeed, unmeasured pollutants such as ozone, carbon monoxide and larger particulate matter may be the source. Researchers theorise that the pollution may be acting on white brain matter – which coordinates communication across the brain. However, there is as yet no scientific evidence to support this theory. Researchers note that less educated males, who saw the largest effect, are the most likely individuals to work outdoors. Weak evidence also suggests a possible correlation between pollution levels and incidence of neurodegenerative disease.



What else declines with age?


 2
2


Balding We still don't really know what causes male-pattern baldness/alopecia. Balding typically happens on the head and is distinct from hair thinning (alopecia), which occurs naturally with age in both males and females when a higher proportion of hair follicles enter the telogen or resting phase, rather than the anagen, or growth phase. Clinical hair loss is classified by the loss of more than 100 hairs a day – a level where regrowth no longer balances loss. Pattern hair loss by age 50 affects about half of males and a quarter of females. Scientists recognise that male-pattern hair loss is caused by a combination of genetics and the male hormone dihydrotestosterone, but how these work and relate to ageingremains a mystery.


We don’t know why shingles – the reactivation of the hibernating varicella zoster virus – happens, although it may be because of age related immune senescence. We also don’t really know what it is: the shingles blister contains the chicken pox (varicella) virus and can cause chicken pox, but you can’t catch shingles from people with chicken pox.


 3
3Animals
As the search for the secret to eternal life continues, scientists have begun to turn to other animals for clues. Various animals have been accused of holding the secret to eternal youth. One of these is the naked mole rat, which lives in East Africa. Most other rodents of its size have short life-spans (up to 4-5 years for mice and rats), but the naked mole rat can live for over 20 years[17]. Scientists are trying to explain why. It may be due to their very low metabolism, and their ability to reduce it further during times of hardship, perhaps helping them deal with oxidative stress better. They also seem to be hugely resistant to cancer – in fact, a naked mole rat with cancer has never been discovered[18]. Mining the secrets of the animal kingdom may be our best bet in our fight to extend our healthy life-span.
As well as looking for animals that naturally live a long time, researchers have found artificial methods of increasing some animals' lifespans. For example, severe calorie restriction allowed mice to live 50% longer than normal[19]. However these gains come at a price. The long-lived mice suffered from reduced fertility and flies bred to live longer don't reproduce as successfully their short-lived counterparts[20]. When it comes to humans, while extending life may seem like a good aim, it wouldn't be so positive if it came at the cost of health. Trials like this are also very difficult to conduct on humans due to the safety risks involved, and the necessarily time-intensive nature of the trial required!


 2
2
Another animal of interest is the whale. The bowhead whale is the longest lived mammal on earth, with a lifespan of more than 200 years. Curiously, it's also much older relative to its whole lifespan when it first contacts age-related diseases, meaning it lives youthfully and healthily for longer. The mechanisms for this longevity and age-related disease resistance are unknown. However, scientists are sure there must be something special about the bowhead whale; for example, given how long they live and how many cells they have in their bodies, they must have a mechanism for resisting cancer, otherwise they'd get it all the time. Scientists are currently studying the bowhead whale genome looking for the answer, which may be useful for relieving age-related illness in humans.


 2
2



Parabiosis As an animal ages, the brain becomes less plastic, leading to cognitive decline. Parabiosis, the process of linking the circulatory systems of a young and old animal so that they share one bloodstream (i.e. stitching rats together) has been practised since the 1860s. Recent work has shown that this treatment carries great benefits for the older animal, including restoring cartilage and muscle, stimulating stem cells and improving memory, fear and spatial learning, and exercise tasks. In particular, hippocampus functionality is rejuvenated. Risks, effects in the younger mice, and potential for application in humans remains to be explored, but this rather weird practice offers a potential window into rejuventive technology.


 2
2Society
The social implications of extending human life are also of great concern. As people live longer, the old outnumber the young, and the question of how we pay for the older generations is raised. Retirement ages will need to rise with life expectancy, but this is only feasible if good mental and physical health are maintained, so people can work for longer. Currently, researchers believe that human lifespan has an upper limit, and life expectancy can’t be extended indefinitely (but they don't agree on the limit itself)[21].


This article was originally published on the TWDK blog, and was written by our Natural Sciences Editor, Ginny Smith, and one of our summer interns from 2013, Johanna Blee.
This article was written by the Things We Don’t Know editorial team, with contributions from Ed Trollope, Ginny Smith, Cait Percy, Johanna Blee, Rowena Fletcher-Wood, Holly Godwin, and Alice Carstairs.
This article was first published on 2015-08-27 and was last updated on 2021-07-16.
References
why don’t all references have links?
[1] Pizza, Vincenzo et al. Neuroinflammation and ageing: current theories and an overview of the data. Reviews on recent clinical trials 6.3 (2011): 189-203. doi: 10.2174/157488711796575577.
[2] Shammas, Masood A. Telomeres, lifestyle, cancer, and aging. Telomeres, lifestyle, cancer, and aging. Current opinion in clinical nutrition and metabolic care. 14.1 (2011): 28. PMCID: PMC3370421. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32834121b1.
[3] Severin, FF, and VP Skulachev. Programmed cell death as a target to interrupt the aging program. Advances in gerontology (Uspekhi Gerontologii) 22.1 (2009): 37. doi: 10.1134/S2079057011010139.
[4] Hawkes, Kristen et al. Grandmothering, menopause, and the evolution of human life histories. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 95.3 (1998): 1336-1339.
[5] Aruoma, OI. Nutrition and health aspects of free radicals and antioxidants. Food and Chemical Toxicology 32.7 (1994): 671-683. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(94)90011-6.
[6] Kaur, Charanjit, and Harish C Kapoor. Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables–the millennium’s health. International Journal of Food Science & Technology 36.7 (2001): 703-725. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2001.00513.x.
[7] Hughes, Adam L., and Daniel E. Gottschling. An early age increase in vacuolar pH limits mitochondrial function and lifespan in yeast. Nature 492.7428 (2012): 261-265. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.11.016.
[8] Hughes, Adam L., and Daniel E. Gottschling. An early age increase in vacuolar pH limits mitochondrial function and lifespan in yeast. Nature 492.7428 (2012): 261-265. doi: 10.1038/nature11654
[9] Epel, Elissa. How Reversible is telomeric aging? Cancer Prevention Research. 5.10 (2012): 1163-1168. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-12-0370.
[10] Slagboom, PE et al. Genomics of human longevity. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 366.1561 (2011): 35-42. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0284.
[11] Nunes, Tiago et al. Familial aggregation in inflammatory bowel disease: Is it genes or environment? World journal of gastroenterology: WJG 17.22 (2011): 2715. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i22.2715.
[12] Yen, Tina WF. Genetic Testing for BRCA Mutations Can Save Lives. Archives of Surgery 146.4 (2011): 479-480.
[13] Xie, Hong-Guang, and Felix W Frueh. Pharmacogenomics steps toward personalized medicine. Future Medicine. 2.4 (2005): 325-337. doi: 10.2217/17410541.2.4.325.
[14] Lillycrop, Karen A. Effect of maternal diet on the epigenome: implications for human metabolic disease. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society. 70.01 (2011): 64-72. doi: 10.1017/S0029665110004027.
[15] Latorre, Eva, et al. Mitochondria-targeted hydrogen sulfide attenuates endothelial senescence by selective induction of splicing factors HNRNPD and SRSF2. Aging (Albany NY) 10.7 (2018): 1666. doi: 10.18632/aging.101500.
[16] Alzheimer’s Society, Factsheet: What is Alzheimer’s disease?
[17] Pérez, Viviana I et al. Protein stability and resistance to oxidative stress are determinants of longevity in the longest-living rodent, the naked mole-rat. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 106.9 (2009): 3059-3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809620106.
[18] Seluanov, Andrei et al. Hypersensitivity to contact inhibition provides a clue to cancer resistance of naked mole-rat. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 106.46 (2009): 19352-19357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905252106.
[19] Weindruch, Richard. The retardation of aging by caloric restriction: studies in rodents and primates. Toxicologic pathology. 24.6 (1996): 742-745. doi: 10.1177/019262339602400618.
[20] Partridge, Linda, and Martin D Brand. Special issue on dietary restriction: dietary restriction, longevity and ageing — the current state of our knowledge and ignorance. Mechanisms of ageing and development 126.9 (2005): 911-912. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2005.03.023.
[21] Carnes, BA, SJ Olshansky, and L Hayflick. Can human biology allow most of us to become centenarians? The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 68.2 (2013): 136-142. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gls142.
Recent aging News
Get customised news updates on your homepage by subscribing to articles